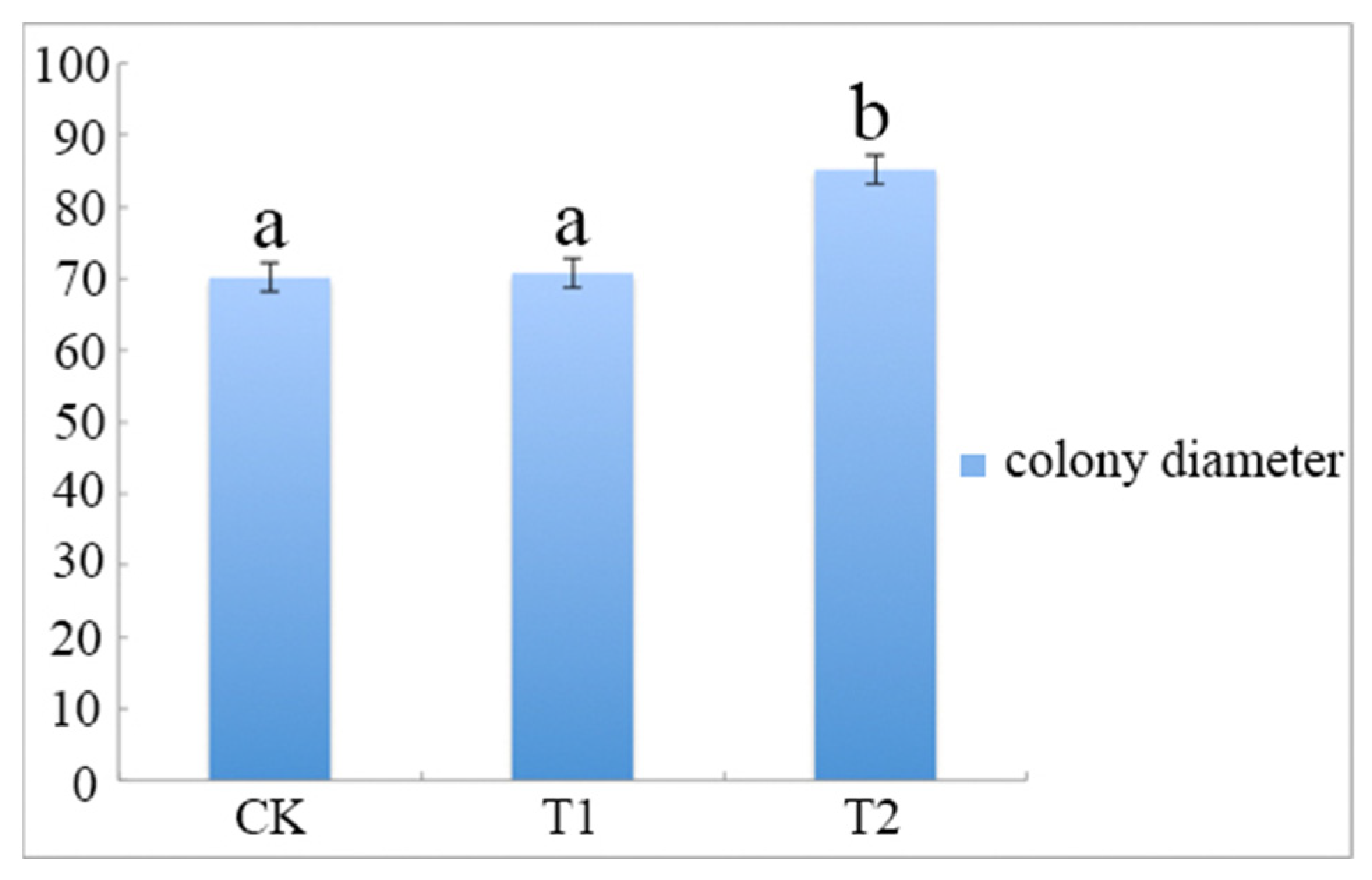


Fifteen strains were resistant to the three azoles tested (24.2%). The strains were highly resistant to the azoles tested (fluconazole, voriconazole and itraconazole). tropicalis resistance to osmotic stress, 85.4% of the isolates were able to grow in a liquid medium containing 15% sodium chloride. In addition, 35 isolates (56.4%) had high hemolytic activity (hemolysis index > 0.55).

The majority of the isolates also showed higher proteinase production than control strains, but low phospholipase activity. Most of the isolates presented wrinkled phenotypes on Spider medium (34 isolates, 54.8%). tropicalis ATCC13803 reference strain, and they also showed increased biofilm production.
In general, environmental isolates were more adherent to human buccal epithelial cells (HBEC) than C. We analyzed 62 environmental isolates and observed a great variation among them for the various virulence factors evaluated. tropicalis isolates from the sandy beach of Ponta Negra, Natal, Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil, regarding the expression of in vitro virulence factors, adaptation to osmotic stress and susceptibility to antifungal drugs. In this context, the objective of this study was to characterize C. These wastes contain various micro-organisms, including Candida tropicalis. Several studies have been developed regarding human health risks associated with the recreational use of beaches contaminated with domestic sewage.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
